中文字体子集化已经是个由来已久的议题,网络上现有的子集化教程一般有两种:一种是爬取页面中使用的文字,并以此进行子集化;另一种是使用现代汉语常用字表等常用字符集进行子集化。
2017 年,Google Fonts 提出了切片字体,用于提高 CJK 字体的加载速度。自 2019 年后,切片字体已经应用于所有的 Noto Sans 网络字体中。本文基于 Google Fonts 的切片字体字符集,展示如何自行生成切片字体。
何为切片字体
CJK 字体由于包含的字符较多,占用容量自然较大,在 Web 中使用一直是一个比较大的问题。
通过 font-spider 等工具爬取页面中使用的文字生成的子集化字体可以做到文件最小化,在应用到页面标题等少量文字的情况下效果很不错。但是,这也有一些问题,例如对于用户输入的文字,API 返回的不确定的文字很难进行有效的子集化。
使用现代汉语常用字表等常用字符集进行子集化是另一种方式,但是规范字表的字符集可能并不能满足使用需要,例如 "囧" 字就不包含在 3500 字字表内。
Google Fonts 团队在 2018 年发表了一篇博文,提出了切片字体方案。
团队首先从数以百万计的日语网页中收集了日文字符的使用频率数据,并对其进行分析。
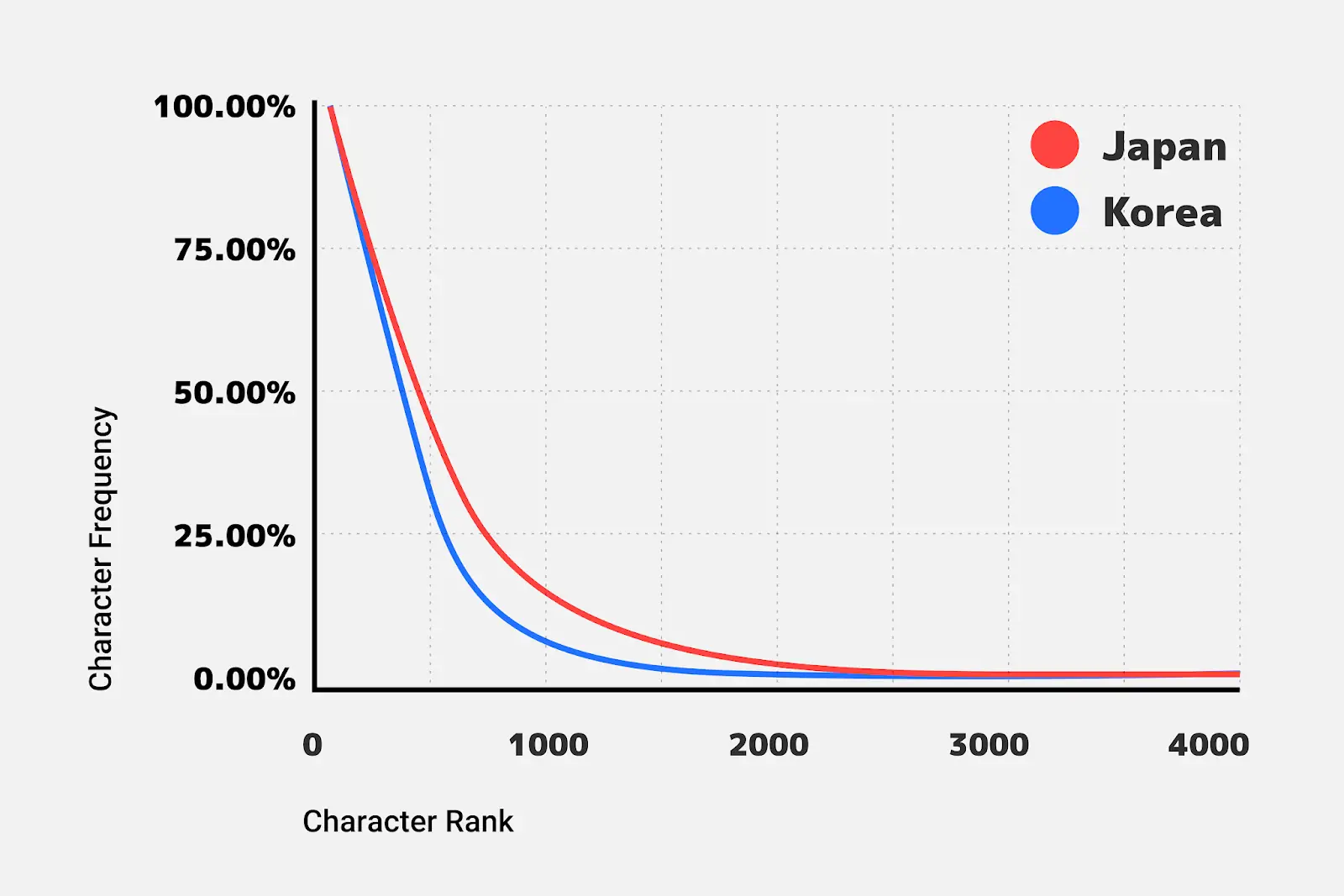
由图可以明显看到,若将图片分为两部分,存在一部分使用频率较高但字符较少的字符集,和一部分使用频率较低但字符较多的字符集 "尾巴"。
由此,团队使用了以下的字符切片策略:
- 将 2000 个最流行的字符放在一个切片中
- 将 1000 个次受欢迎的字符放在另一个切片中
- 按 Unicode 编码对剩下的字符进行分类,并将它们分成 100 个大小相同的切片
用户在浏览网页时,只需下载页面上的字符所需的切片。根据团队的统计结果,这种情况下下载的字节数比发送整个字体少了 88%。进一步的,切片字体依赖的核心功能是 unicode-range 和 woff2,而支持这两项功能的浏览器也支持 HTTP/2,HTTP/2 可以实现许多小文件的同时传输。
为此,针对韩文字体,团队做了进一步的改进:
- 将 2000 个最流行的字符放在 20 个相同大小的切片中
- 按 Unicode 编码对剩下的字符进行分类,并将它们分成 100 个大小相同的切片
根据团队的统计结果,这种情况下下载的字节数比之前的最佳策略少了 38%。
最终,团队将这样的切片字体策略应用到了 CJK 字体中,并且针对不同语言调整了字符集大小和切片大小。
环境需求
以下是进行本文所述操作需要的系统环境要求:
- Node.js >= 18
- Python >= 3.7
获取字符集
我们无法直接了解到 Google Fonts 团队获取的字符集,但是我们可以获取到 Google Fonts 中 Noto 家族字体的 CSS 文件,并从中提取出字符集。
需要注意的一点是 Google Fonts API 仅当浏览器支持所需的特性时才会返回切片字符集 CSS。首先获取 CSS 并匹配出 unicode-range。
const url = 'https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Noto+Sans+SC';
const ua =
'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:101.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/101.0';
/**
* get css from google fonts
* @returns {Promise<string>}
*/
async function getCSS() {
const res = await fetch(url, {
headers: { 'User-Agent': ua },
});
const css = await res.text();
return css;
}
/**
* get unicode ranges from css
* @param {string} css
* @returns {any}
*/
function getUnicodeRanges(css) {
css = css.replace(/\n/g, '');
const idExp = /(\[[0-9]+\])/gi;
const rangeExp = /unicode-range: ([^;]+);/gi;
let idExpr = idExp.exec(css);
let rangeExpr = rangeExp.exec(css);
const res = {};
while (idExpr && rangeExpr && idExpr[1] && rangeExpr[1]) {
res[idExpr[1]] = rangeExpr[1].replace(/ /g, '');
idExpr = idExp.exec(css);
rangeExpr = rangeExp.exec(css);
}
if (Object.keys(res).length === 0) {
return null;
}
return res;
}
const css = await getCSS();
const ranges = getUnicodeRanges(css);
在获取到切片 ID 和对应的 unicode-range 后,对 unicode-range 中使用 - 连接的范围进行拆分以备后面去重使用:
/**
* replace unicode range to individual unicode
* @param {string} range
* @returns {string[]}
*/
function parseUnicodeRange(range) {
const rangeArr = range.split(',');
const res = [];
rangeArr.forEach((item) => {
if (!item.includes('-')) {
res.push(item);
} else {
const tempArr = /U\+([0-9A-F]+)-([0-9A-F]+)/i.exec(item);
const startInt = Number.parseInt(tempArr[1], 16);
const endInt = Number.parseInt(tempArr[2], 16);
for (let i = startInt; i <= endInt; i++) {
const hex = i.toString(16);
res.push('U+' + hex);
}
}
});
return res;
}
Object.entries(ranges).forEach(([id, range]) => {
const unicodeArr = parseUnicodeRange(range);
ranges[id] = unicodeArr;
});
fse.writeJSONSync(path.resolve(__dirname, '../raw/ranges.json'), ranges, {
spaces: 2,
});
完成后,获得了如下的 JSON 文件,包含了每个切片的 ID 和对应的字符集:
{
"[4]": ["U+1f1e9", "U+1f1ea"],
"[5]": ["U+fee3", "U+fef3", "U+ff03", "U+ff04", "U+ff07"],
"[6]": ["U+f0a7", "U+f0b2", "U+f0b7"]
}
过滤有效字符
获取的字符集所包含的字符并不一定被需要切片的字体支持,因此需要过滤掉不支持的字符。
字体 CMAP 表中包含了支持的字符,通过解析 CMAP 表进行过滤操作。CMAP 表的提取通过 Python 工具包 fonttools 实现。
// output of `fetch.js` script
const ranges = fse.readJSONSync(path.resolve(__dirname, '../raw/ranges.json'));
/**
* get all supported unicodes of a font file
* @returns {Promise<Set<string>>}
*/
async function getSupportedUnicodeSet(file) {
// get cmap ttx with fonttools
const ttxFile = file.replace(/\.ttf$/, '.ttx');
childProcess.execSync(`fonttools ttx -t cmap -o ${ttxFile} ${file}`);
const cmap = fse.readFileSync(ttxFile, 'utf-8');
// match unicodes
const unicodeSet = new Set();
const exp = /<map +code="([^"]+)"/gi;
let expr = exp.exec(cmap);
while (expr && expr[1]) {
const str = expr[1];
const unicode = str.toLowerCase().replace(/^0x/, 'U+');
unicodeSet.add(unicode);
expr = exp.exec(cmap);
}
// remove ttx file
fse.unlinkSync(ttxFile);
return unicodeSet;
}
// get all supported unicodes
const supportedUnicodeSet = await getSupportedUnicodeSet(file);
// filter the ranges
const rangesOfThisFile = { ...ranges };
const processedUnicodeSet = new Set();
Object.entries(rangesOfThisFile).forEach(([key, unicodes]) => {
// filter the unicodes
const supportedUnicodes = unicodes.filter((unicode) =>
supportedUnicodeSet.has(unicode)
);
// if no unicode is supported, delete the range
if (supportedUnicodes.length === 0) {
delete rangesOfThisFile[key];
} // if some unicode is supported, update the range
else {
rangesOfThisFile[key] = supportedUnicodes;
// mark supported unicodes as processed
supportedUnicodes.forEach((unicode) => processedUnicodeSet.add(unicode));
}
});
// mark those unicodes supported in font but not processed
const unProcessedUnicodeSet = new Set();
Array.from(supportedUnicodeSet).forEach((unicode) => {
if (!processedUnicodeSet.has(unicode)) {
unProcessedUnicodeSet.add(unicode);
}
});
// write the result to json
fse.writeJSONSync(
path.resolve(__dirname, '../raw/ranges-supported.json'),
rangesOfThisFile,
{ spaces: 2 }
);
fse.writeJSONSync(
path.resolve(__dirname, '../raw/ranges-unprocessed.json'),
Array.from(unProcessedUnicodeSet),
{ spaces: 2 }
);
完成后,获得了两张表,分别是字体支持且包含在切片中的字符集和字体支持的但是不包含在切片中的字符集。
字体切片
对于字体支持且包含在切片中的字符集,按照字符集切片即可;对于字体支持的但是不包含在切片中的字符集,可以直接忽略,或是自己设计切片策略进行进一步的补充切片。
首先为补充切片生成 unicode-range,使用负下标作为索引:
/**
* @param {Set<string>} set
*/
async function sliceUnprocessedUnicodes(set) {
const arr = Array.from(set).sort((a, b) => u2n(a) - u2n(b));
// 140 char per slice
const slices = {};
let idx = 1;
slices[`[-${idx}]`] = [];
for (const u of arr) {
if (slices[`[-${idx}]`].length >= 140) {
idx++;
slices[`[-${idx}]`] = [];
} else {
slices[`[-${idx}]`].push(u);
}
}
// if last slice is to small
if (slices[`[-${idx}]`].length < 100) {
slices[`[-${idx - 1}]`] = [
...slices[`[-${idx - 1}]`],
...slices[`[-${idx}]`],
];
delete slices[`[-${idx}]`];
}
return slices;
}
// custom slices
const customSlices = await sliceUnprocessedUnicodes(unProcessedUnicodeSet);
fse.writeJSONSync(
path.resolve(__dirname, '../raw/ranges-custom.json'),
customSlices,
{ spaces: 2 }
);
定义一些工具方法,例如计算字体文件哈希、Unicode 编码转数字、合并 CSS Unicode 范围等:
/**
* get hash of a font file
* @param {string} file
* @returns {string}
*/
function getHash(file) {
const hasher = crypto.createHash('sha1');
hasher.update(fse.readFileSync(file));
return hasher.digest('hex');
}
/**
* unicode (hex) to number
* @param {string} u
* @returns {number}
*/
function u2n(u) {
return Number.parseInt(/U\+([0-9A-F]+)/i.exec(u)[1], 16);
}
/**
* merge sequential unicodes for css
* @param {string[]} unicodes
* @returns {string}
*/
function mergeUnicodes(unicodes) {
unicodes = [...unicodes].sort((a, b) => u2n(a) - u2n(b));
const merged = [];
let start = null;
let end = null;
for (const cur of unicodes) {
if (start === null) {
start = cur;
end = cur;
} else if (u2n(end) === u2n(cur) - 1) {
end = cur;
} else {
merged.push(start === end ? start : `${start}-${u2n(end).toString(16)}`);
start = cur;
end = cur;
}
}
if (start !== null) {
merged.push(start === end ? start : `${start}-${u2n(end).toString(16)}`);
}
return merged.join(',');
}
随后设定一些初始化变量,例如输出目录,输出文件名等:
const hash = getHash(file).substring(0, 8);
const outFile = file.replace(/\.ttf$/, `.subset.ttf`);
const baseName = path.basename(file, '.ttf');
const targetFolder = path.resolve(__dirname, '../raw/subset');
const fontWeight = baseName.split('-')[1];
let css = '';
fse.ensureDirSync(targetFolder);
if (!empty) {
fse.emptyDirSync(targetFolder);
empty = true;
}
最后进行切片,流程如下:
- 合并支持字符串的字符集和自定义补充切片的字符集
- 创建切片为
<fontname>.subset.ttf - 移动切片文件为
<basename>.<hash>.<index>.woff2 - 为包含/不包含补充切片创建两个 CSS
<basename>.[slim].min.css
// create subsets
Object.entries({ ...rangesOfThisFile, ...customSlices }).forEach(
([key, unicodes]) => {
const _unicodes = unicodes.join(',');
childProcess.execSync(`fonttools subset --unicodes="${_unicodes}" ${file}`);
// move subset to the output directory
const index = /\[(-?[0-9]+)\]/i.exec(key)[1];
const targetFile = path.resolve(
targetFolder,
`${baseName}.${hash}.${index}.ttf`
);
fse.moveSync(outFile, targetFile);
childProcess.execSync(`fonttools ttLib.woff2 compress ${targetFile}`);
fse.unlinkSync(targetFile);
css +=
`/*${key}*/` +
`@font-face{font-family:MiSans;font-style:normal;` +
`font-weight:${fontWeight};font-display:swap;` +
`src: url('${baseName}.${hash}.${index}.woff2') format('woff2');` +
`unicode-range:${mergeUnicodes(unicodes)};}\n`;
}
);
fse.writeFileSync(
path.resolve(targetFolder, `${baseName}.min.css`),
css.trim(),
'utf-8'
);
const cssWithoutCustom = css
.trim()
.split('\n')
.filter((line) => !line.includes('/*[-'))
.join('\n');
fse.writeFileSync(
path.resolve(targetFolder, `${baseName}.slim.min.css`),
cssWithoutCustom,
'utf-8'
);
切片完成后,即可获得切片文件和 CSS:
misans-100-thin.c6513dc3.-1.woff2
misans-100-thin.c6513dc3.-2.woff2
misans-100-thin.c6513dc3.-3.woff2
...
misans-100-thin.c6513dc3.118.woff2
misans-100-thin.c6513dc3.119.woff2
misans-100-thin.c6513dc3.119.woff2
misans-100-thin.c6513dc3.119.woff2
misans-100-thin.min.css
misans-100-thin.slim.min.css
misans-200-extralight.21as24sf.-1.woff2
misans-200-extralight.21as24sf.-2.woff2
...
MiSans 切片字体
本文的提取和切片方法已应用于作者本人发布的 MiSans Web 字体中。切片操作的完整代码实现也以 Apache-2.0 License 发布于仓库。
